Your mind and your body deserve the same positive care. This article delves into the role of nutrition in addressing low mood, highlighting specific dietary changes and supplements that can help.
Food & Mood: Well-being Nutrition for Mental Well-being
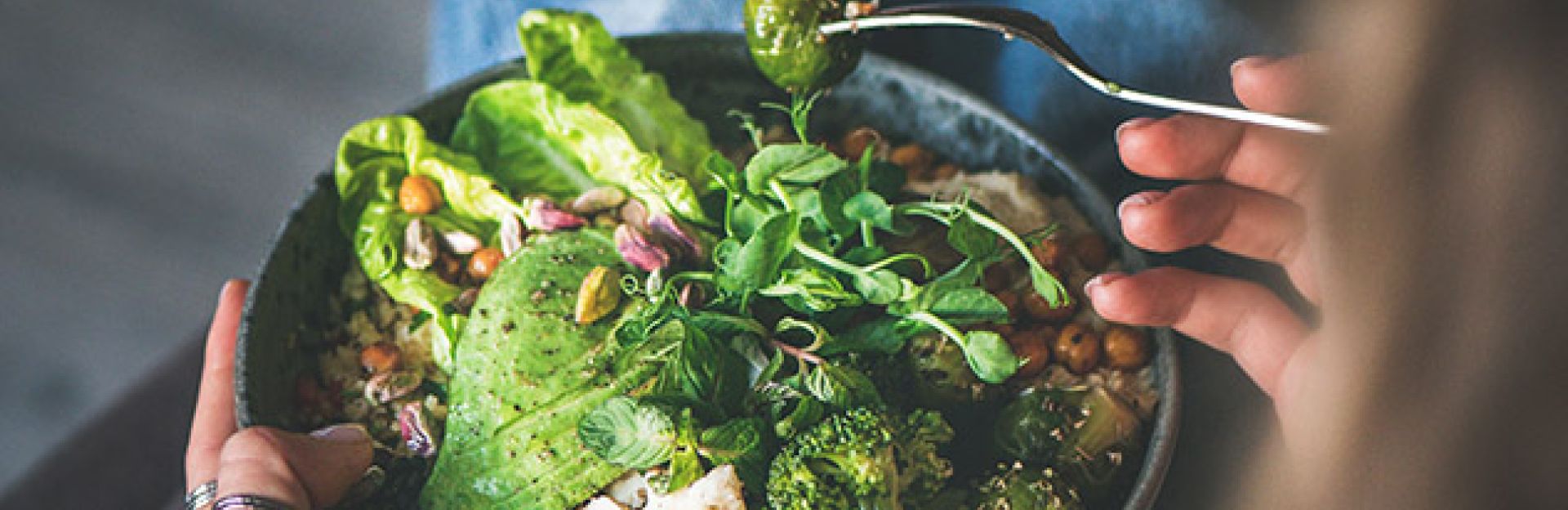
There is a growing amount of attention on the implications between nutrition and mental health. Research has shown that eating a healthier diet that includes the right balance of fats, prioritizes protein in every meal, and has a high consumption of fruits and vegetables, will help boost optimal brain function.
In 2023, the American Psychiatric Association surveyed 2,200 adults and found that 66% feel “knowledgable” about the relationship between their personal diet and mental health, but only 43% said they would be “very willing” to make a diet change to improve their mental health. It may feel overwhelming how to start, so what would this change look like?
Fruits and Vegetables
It has been shown that an increase in fruit and vegetable consumption positively impacts psychology health. Fruits and vegetables are recognized as a key and essential part of a healthy diet as they contain many important vitamins and minerals.
Supplements are another way to get these key vitamins and minerals. It may feel overwhelming on where to start because of the wide variety of supplements, but having many options means you can tailor them to your specific needs. A great way to introduce yourself is to take a multivitamin and a probiotic. You can find many multivitamins that fit your basic needs and, as we will discuss in a moment, taking a probiotic can positively impact your digestive and gut health: which can be key in improving mental wellbeing.
From there, you can expand to other supplements and vitamins based on your individual needs.*
Gut Health
But a healthy diet goes beyond fruits and vegetables. In a 2022 Harvard Health Blog, Eve Selhub MD speaks about gut health. 95% of our serotonin, the neurotransmitter that contributes to mood, sleep, and appetite regulation, is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Your gastrointestinal tract contains millions of neurons that work with the “good” bacteria in your gut to help you absorb nutrients and limit inflammation, create barriers against “bad” bacteria, and communicate signals through a direct neurological pathway to your brain. Your diet heavily affects the health of these neurons and bacteria. Researchers have found that those who eat along the Mediterranean or Japanese diets have a 25% to 30% reduced risk of depression.
Our mind and body are intrinsically linked in many ways. Your mind deserves the same care you give your body. Also caring for your mind through diet can not only improve your mental well-being but also your physical performance.
*As always, check with a trusted medical professional before making any big changes to your use of supplements.
Word Count: 471
Reading Time: 2 minutes